What's New
Quantum SDK Is Now A Unitypackage
Moving to a Unitypackage makes the initial setup and upgrades easier for everyone, and lays the groundwork for future distribution of Quantum via the Asset Store and/or UPM.
- The source for
QuantumGame(formerly known as the quantum.code project) now resides in the Unity Assets folder:Assets/QuantumUser/Simulation/. - Unity CodeGen step has been removed, all the code generation is now done by the Qtn/DSL CodeGen and inside Unity Editor.
- To clean up the Unity integration, a significant number of Quantum types and scripts have been moved, renamed and merged. During migration, script GUIDs are preserved and to reduce the number of compilation errors, obsolete scripts with legacy names are provided with
QUANTUM_ENABLED_MIGRATION. - Unity/Odin property attributes can be used at will. This includes
[SerializeReference]and Odin-specific serialization extensions. Any use of non-deterministic Unity API is still strongly discouraged. - New assets are given a deterministic
AssetGuid. This allows all possible Quantum assets to be collected without loading their contents, dramatically speeding up the process. AssetBaseis no longer needed:AssetObjects are alreadyScriptableObjects. This makes asset hierarchies more flexible and no longer limited to partial extensions model for Unity-only properties.- The minimum Unity Version was increased to
2021 LTSto reduce the amount of legacy code.
It's still possible to compile a simulation dll without Unity dependencies for example to run on a .Net console application or on a custom server plugin. Use the QuantumDotnetBuildSettings to generate and compile it.
See the Quantum Project for details about the SDK content.
New Quantum Assembly Names
The following Quantum libraries have been renamed:
PhotonDeterministic.dll->Quantum.Deterministic.dllquantum.core.dll->Quantum.Engine.dllquantum.code.dll->Quantum.Simulation.dll
Input Delta Compression
Input messages are now delta compressed by default, significantly reducing overall bandwidth. The network transport mode for server messages has been changed to reliable, simplifying the Quantum input protocol.
Raw input mode is still supported, but delta compression is enabled by default.
Replays also store delta-compressed input and are now significantly smaller.
New Protocol For Adding And Removing Players
The Quantum startup protocol has been modified to allow players to be added and removed at run time without having to reserve seats at the start.
AddPlayer() and RemovePlayer() replace the method SendPlayerData(). Unlike SendPlayerData(), AddPlayer() can only be sent once per player slot.
The simulation can react to added and removed players with the ISignalOnPlayerAdded and ISignalOnPlayerRemoved signals.
The view can react to local player slots being added with CallbackLocalPlayerAddConfirmed and OnLocalPlayerRemoveConfirmed as well as errors by listening for OnLocalPlayerAddFailed and OnLocalPlayerRemoveFailed.
AddPlayer() has a rate limit on the server and cannot be spammed.
Throughout the API, the wording of parameters has been slightly changed to better differentiate between players (PlayerRef) and player slots (local players).
A Player always refers to the actual global player index, while PlayerSlot always refers to a local player slot, used for example when controlling multiple players from one client. If only one local player slot is used, it will be slot `0'.
The input callback CallbackPollInput for example now uses the PlayerSlot property. QuantumGame.AddPlayer(Int32 playerSlot, RuntimePlayer data) explicitly names the parameter to identify as a local player slot.
More information in the Player Manual
Predicted Commands
Command are now immediately available on the next predicted frames. This has been a feature request for some time, and it made sense to add it now that there is a new version and improved input protocol.
When sending commands, they will now be added to the next prediction frame and will be available during non-verified frames. The actual predicted tick number should be close to 99.9% accurate.
This allows commands to be more responsive and reflect gameplay changes much faster.
Webhooks
Webhooks are an enhancement to secure games with a custom backend: room creation, room joining, RuntimePlayer, RuntimeConfig can be intercepted and validated by a backend using HTTP requests.
Webhooks also allow replay streaming directly from the server.
They are activated and configured via the Photon dashboard.
See the Webhook Online API Documentation for more information.
Quantum 3 AppIds
Quantum 3 applications require the explicit creation of a Quantum 3 AppId on the Photon Dashboard.
Read the Quantum Asteroids Tutorial - Project Setup tutorial for more information.
Photon Realtime 5
The new major version of Realtime includes .Net async extensions to improve writing and handling of network connections.
Be sure to read the Photon Realtime release notes found under:
To start a Photon client connection and join a Photon room, just call one method and awaited:
C#
MatchmakingArguments connectionArguments = new MatchmakingArguments {
PhotonSettings = PhotonServerSettings.Default.AppSettings,
PluginName = "QuantumPlugin",
MaxPlayers = 8,
UserId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
NetworkClient = new RealtimeClient { ClientType = ClientAppType.Quantum }
};
RealtimeClient client = await MatchmakingExtensions.ConnectToRoomAsync(connectionArguments);
By default, all errors are thrown as exceptions. Calls to the async API must be wrapped in try/catch blocks.
More information about the Realtime extensions are found in the Photon Async Extensions.
The SessionRunner Class
QuantumRunner and SessionContainer have been merged into the SessionRunner class which is located in the Quantum Game project. It uses the new Photon Realtime 5 library.
Quantum game sessions can be started in an async and non-async mode:
C#
SessionRunner.Arguments sessionRunnerArguments = new SessionRunner.Arguments {
RunnerFactory = QuantumRunnerUnityFactory.DefaultFactory,
GameParameters = QuantumRunnerUnityFactory.CreateGameParameters,
ClientId = client.UserId,
RuntimeConfig = runtimeConfig,
SessionConfig = QuantumDeterministicSessionConfigAsset.DefaultConfig,
GameMode = DeterministicGameMode.Multiplayer,
PlayerCount = 8,
StartGameTimeoutInSeconds = 10,
Communicator = new QuantumNetworkCommunicator(client),
};
QuantumRunner runner = (QuantumRunner)await SessionRunner.StartAsync(sessionRunnerArguments);
Awaiting the start will resume when the Quantum start protocol has finished and any snapshots have been received.
Try out the QuantumSampleConnection.unity scene for the simplest way to connect and start an online Quantum simulation.
New SDK Sample
The new SDK comes with a simple gray-boxing Asteroids game example that can be installed with the QuantumHub.
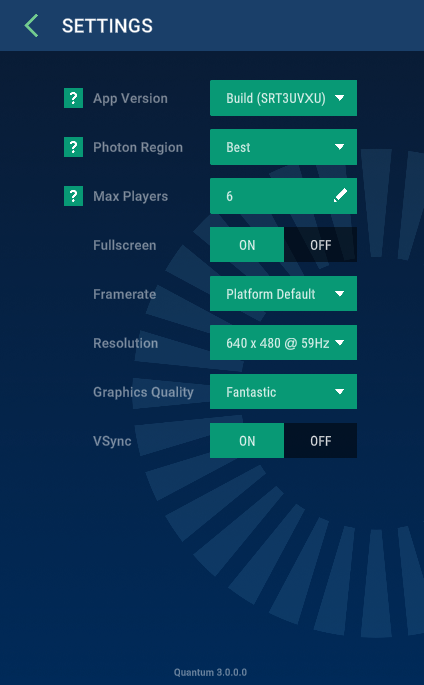
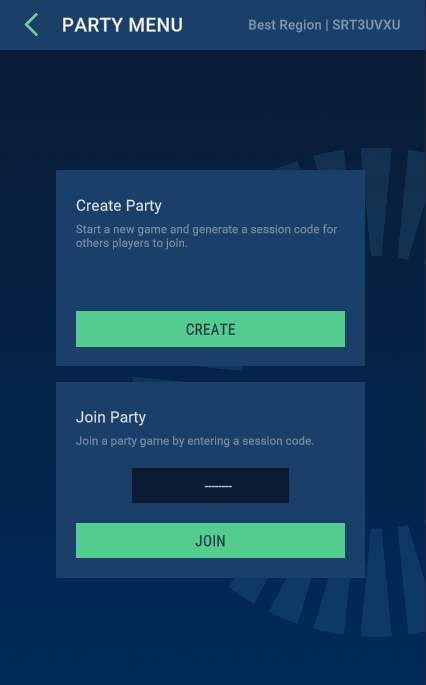
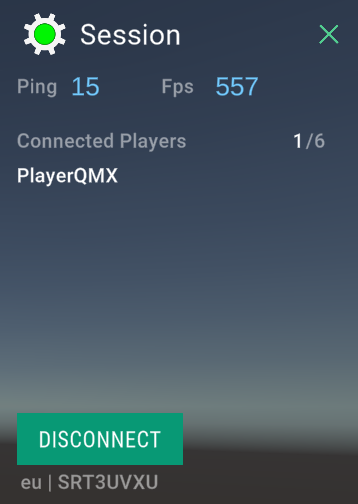
New Demo Menu
The new demo menu replaces the sample lobby menu from Quantum 2.1. It has received a graphical upgrade (in Unity.UI) and implements two simple online modes: random matchmaking and party-code sharing.
The demo menu code and prefabs are distributed with the SDK in a `unitypackage`` and can be installed using the QuantumHub Tutorials&Sample section.
It has been designed to be extensible and to handle the complexity of the connection logic. These design goals compete with each other and this solution tries to balance them reasonably. Parts of the menu implementation and prefabs are also used by other SDKs such as Fusion.

|
|
|

|
|
The demo scene uses TextMeshPro. When the demo scene is opened for the first time, the TMP installation popup is displayed.
The Quantum menu scripts will compile even if TMP is disabled: The Quantum.Unity assembly definition will set the QUANTUM_ENABLE_TEXTMESHPRO when the TMP Unity package (com.unity.textmeshpro) is found.
Read here for information on how to customize the menu: Sample Menu Customization
RuntimeConfig And RuntimePlayer Json Serialization
Manual serialization of these files has been replaced by Json. The configs are still sent over the Quantum protocol, but as compressed Json strings.
The original serialization always required manual maintenance, which was cumbersome and a source of errors. In addition, when passing the configs via HTTP requests for webhooks, the receiving backend would need to have the original C# code to deserialize it correctly.
The SerializeUserData() method is now deprecated.
To serialize the configs to a byte array, the QuantumGame.RuntimePlayerSerializer is required, which is set when starting a runner with SessionRunner.Arguments and is usually set to the default Quantum Json serializer `QuantumJsonSerializer'.
C#
var runtimeConfig = new RuntimeConfig();
var runtimeConfigBinary = RuntimePlayer.ToByteArray(runtimeConfig, new QuantumJsonSerializer());
var runtimeConfigOther = RuntimePlayer.FromByteArray(runtimeConfigBinary, new QuantumJsonSerializer());
// make sure to check if runtimeConfig and runtimeConfigOther are equal to validate the json serialization
The maximum size for a serialized binary RuntimePlayer (or commands) is 24 kB. Additionally, if multiple clients send large chunks of data this way and they do not fit into one input message, they will be accepted by the server in successive ticks.
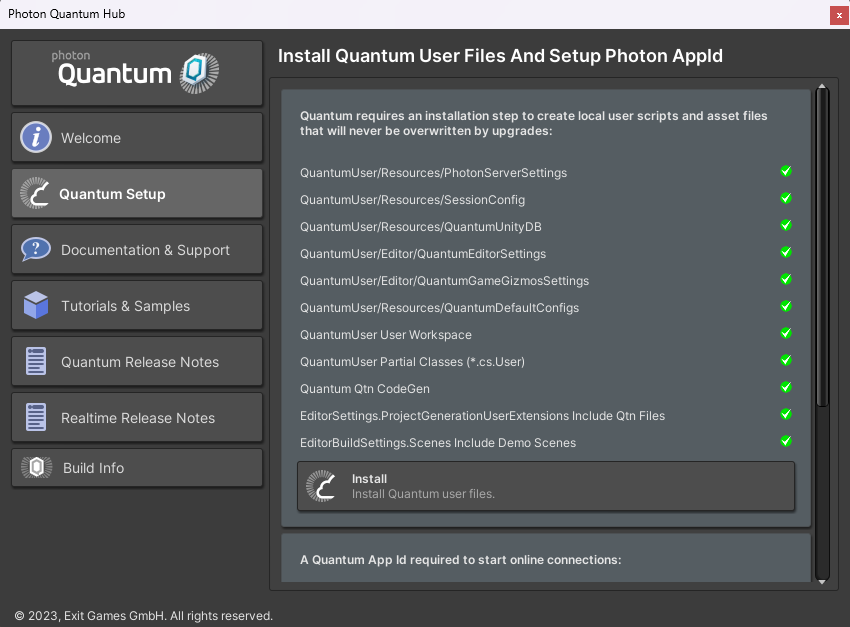
Quantum Hub
The Quantum Hub pops up when critical configuration files cannot be found. The Fusion SDK has proven that using a Hub window is the most convenient way to install and generate user files (which are not included in the package). This setup only needs to be done once, and the resulting files are kept in version control with the rest of the project.
Quantum CodeDoc Inspectors
The Quantum Unity inspectors got a visual upgrade and will include toggle-able help text which is generated from inline XML code comments.
Data-Driven System Setup
The selection of Quantum systems to start can vary depending on the game mode or map selection. A data-driven approach is introduced using the SystemsConfig asset. Different combinations of systems and subsystems combined in a Quantum asset can now be referenced by the RuntimeConfig asset.
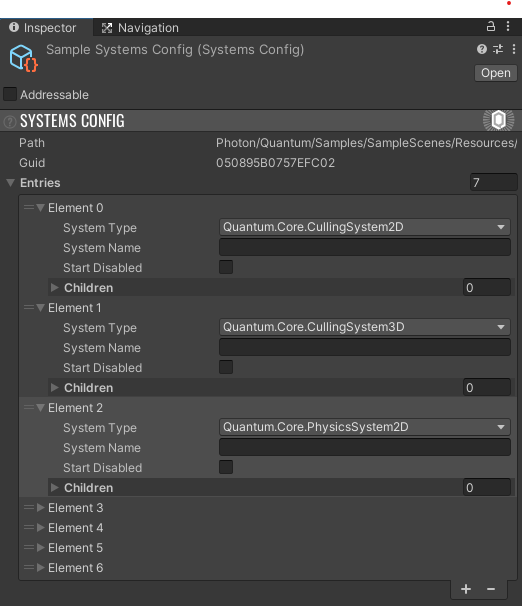
The Quantum 2.1 static SystemSetup.CreateSystems() still works, but is considered deprecated and will log a warning. The class can be deleted after upgrading a Quantum 2.1 project and migrating the content.
Systems get created in this order (see DeterministicSystemSetup.CreateSystems()):
- The old
SystemSetup.CreateSystems()class and method exists (checked by reflection) -> call and and skip the rest - Provided
SystemsConfighas entries -> create and add systems and continue - Provided
SystemConfigis invalid or has no entries -> create and add default systems and continue - Finally the partial user method is called
DeterministicSystemSetup.AddSystemsUser()to allow final touches
Old: file: quantum_code/quantum.code/SystemSetup.cs
C#
namespace Quantum {
public static class SystemSetup {
public static SystemBase[] CreateSystems(RuntimeConfig gameConfig, SimulationConfig simulationConfig) {
return new SystemBase[] {
// ..
}
}
}
}
New: file: Assets/QuantumUser/Simulation/SystemSetup.User.cs
C#
namespace Quantum {
using System.Collections.Generic;
public static partial class DeterministicSystemSetup {
static partial void AddSystemsUser(ICollection<SystemBase> systems, RuntimeConfig gameConfig, SimulationConfig simulationConfig, SystemsConfig systemsConfig) {
systems.Add(new TestSystemMainThreadGroup("TestSystemsGroup", new SystemMainThread[] { new TestSystemImmediateRemoveDestroy(), }));
systems.Add(new TasksTestSystem());
3D Capsule Shape
Finally Quantum physics supports for 2D and 3D capsule shapes.
Max Components
Increasing the max component count to 512 can be now configued inside a qtn-file:
#pragma max_components 512
Entity View Framework
Use the Unity script EntityViewComponent to quickly add view code that can quickly inspect and react to the game state.
Entity View Pool
Entity view can be easily pooled using the QuantumEntityViewPool.
Character Controller Addon
A new iteration of the kinematic character controller based on the new capsule collision checks is available as an add-on.
Partly Deterministic Navmesh Baking
The Quantum navmesh baking is now deterministic, which is interesting for games that generate a navmesh at runtime. The default pipeline still relies on importing a Unity mesh (non-deterministic). A replacement will come eventually.
Navmesh baking has been moved from Unity to the simulation code in QuantumGame (see individual release note changes).
Dashboard Options
By default, Quantum3 applications block non-protocol messages and player properties. Leaving these legacy features open could potentially allow malicious actors to disrupt the matchmaking and gameplay flow of Quantum apps, even if the actual gameplay cannot be disrupted. To unlock these features, they must be explicitly set in the dashboard properties for individual AppIds.
BlockNonProtocolMessages(true/false)BlockPlayerProperties(true/false)
BlockRoomProperties (New)
Type: boolean (true/false)
The plugin will cancel all room properties set by clients after the room creation. With the exception of a property named StartQuantum. Initial room properties can also be retrieved with a webhook.
Caveat: This affects Open and IsVisible as well.
AllowedLobbyProperties (New)
Type: string (Allowed separators: , or ; or space)
Maximum number of properties: 3
Maximum string property length: 64
Set a list of properties that the client is allowed to send as lobby properties to protect the matchmaking performance on the master servers. If this property is set, non-listed properties sent by clients will be stripped. The plugin logs Restricted LobbyProperty once found.
Additionally by default the property types are restricted to: bool, byte, short, int, long, string
MaxPlayerSlots (New)
Type: int
By default, clients can create as many local players as the game supports. Setting this value will limit this for all games running under this AppId. This value can also be set by the webhooks.
StartPropertyBlockedTimeSec (New)
Type: int
If set to a number greater than zero, Quantum will be blocked from starting in a room until the minimum number of seconds has passed since the room was created. This can be used to ensure that players have enough time to join before the game starts.
StartPropertyForcedTimeSec (New)
Type: int
If set to a number greater than zero, this is the maximum number of seconds that can elapse after the room is created before Quantum is started in the room. If the specified time is exceeded, the game will set the StartQuantum property in the room's game properties to true if it hasn't already been set.
HideRoomAfterStartSec (New)
Type: int
If set to a number greater than zero, it defines the number of seconds after which the room will be hidden from public or search listings once Quantum is started in the room. This can help manage room visibility and ensure that new players do not join games already in progress.
CloseRoomAfterStartSec (New)
Type: int
If set to a number greater than zero, it determines the number of seconds after which the room will be closed after Quantum is started in the room. Closing a room prevents new players from joining and can be used to manage the lifecycle of the game session.
Back to top- Quantum SDK Is Now A Unitypackage
- New Quantum Assembly Names
- Input Delta Compression
- New Protocol For Adding And Removing Players
- Predicted Commands
- Webhooks
- Quantum 3 AppIds
- Photon Realtime 5
- The SessionRunner Class
- New SDK Sample
- New Demo Menu
- RuntimeConfig And RuntimePlayer Json Serialization
- Quantum Hub
- Quantum CodeDoc Inspectors
- Data-Driven System Setup
- 3D Capsule Shape
- Max Components
- Entity View Framework
- Entity View Pool
- Character Controller Addon
- Partly Deterministic Navmesh Baking
- Dashboard Options