Simulating Network Conditions
Overview
When testing locally, it is advisable to always test networking code under realistic or even worse than realistic latency and loss. Much of the complexity of good networked game design revolves around how the paradoxes and time differences between players are hidden. This allows to be aware of the actual player experience the codebase will produce.
To this end test should either be run with real internet connections or simulated if the development pipeline requires building and testing locally.
Fusion has built in Network Condition simulation which is available when using the debug version of the fusion.dll. When using the release dll, the use of external software such as Clumsy for Windows is required.
Built-in Network Conditions
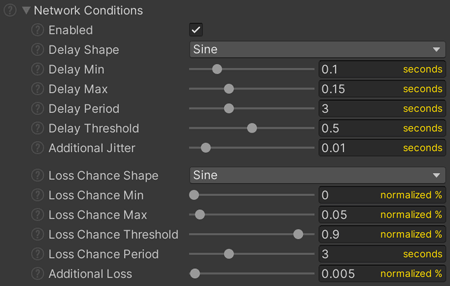
The built-in Network Conditions operatates with a combination of oscillators for Delay (latency) and Loss and random value generators. These oscillators allow for the simulation of Delay and Loss using values which vary over time (to allow simulation of VERY terrible internet conditions such as intermittent congestion). If fixed values are preferred over oscillation, just set the Min and Max values to match.
Enabling Network Conditions
- Open the
NetworkProjectConfig(Unity menuFusion > Network Project Config). - Find the foldout named
Network Conditions.- If the foldout is not visible, the project is most likely currently using the release
fusion.dll. In this case, switch to the debug dll by navigating to the Unity menuFusion > Toggle Debug Dlls. N.B.: A Unity Editor restart may be required for the change to take effect.
- If the foldout is not visible, the project is most likely currently using the release
- Toggle
Enabledto enable and disable network condition simulation.
Settings
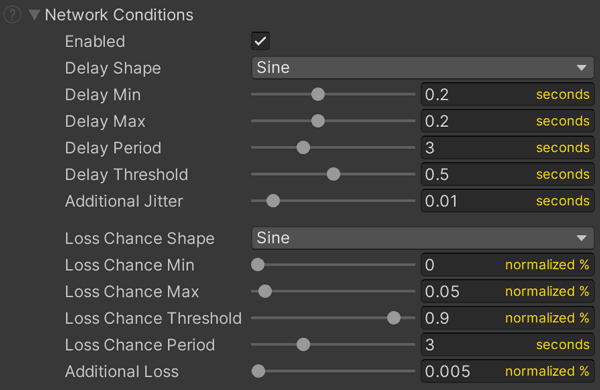
Network Conditions
- Enabled: If adverse network conditions are being simulated.
- Delay Shape: The pattern used to oscillate between
DelayMinandDelayMaxvalues. - Delay Min: The lowest packet delay value returned from the
DelayShapeoscillator. - Delay Max: The highest packet delay value returned from the
DelayShapeoscillator. - Delay Period: The period of the
DelayShapeoscillator (the rate at which delay oscillates in seconds). - Delay Threshold: The
DelayShapeoscillates between 0 and 1. Values below this threshold are reduced to zero, resulting in a value equal toDelayMin. - Additional Jitter: After the delay value from the
DelayShapeoscillator is determined, an additional random value between 0 and thisAdditionalJitteris added to the delay time. - Loss Chance Shape: The pattern used to oscillate between
LossChanceMinandLossChanceMaxvalues. - Loss Chance Min: The lowest loss chance value the
LossChanceShapeoscillator will produce. 0 = 0% chance of being lost. 1 = 100% chance of being lost. - Loss Chance Max: The highest loss chance value the
LossChanceShapeoscillator will produce. 0 = 0% chance of being lost. 1 = 100% chance of being lost. - Loss Chance Threshold: The
LossChanceShapewave oscillates between 0 and 1. Values below this threshold are reduced to zero, resulting in a value equal toLossChanceMin. - Loss Chance Period: The period of the
LossChanceShapeoscillator (the rate at which delay oscillates in seconds). - Additional Loss: After a loss chance value is generated by the
LossChanceShapeoscillator, an additional random value between 0 and thisAdditionalLosswill be added to the (normalized) loss chance.
Host and Server Mode
The built-in Network Conditions produce 1/2 of the indicated values on each peer. Both the server and the client apply these values, resulting in total latency resulting about equal to the setting. In other words, a delay of 200ms will result in:
- the Server holding packets for ~100ms; and,
- the clients holding their packets for ~100ms.
Shared Mode
In Shared Mode, clients always connect to online the Photon Game Servers. When testing in Shared Mode, the network conditions do not need to be simulated as the local client is seeing actual online play.
However, it may still be desirable to add some latency and loss to simulate worse conditions than the current connection offers. Be aware, in Shared Mode only the clients are adding simulated latency and loss, so only half (50%) of the indicated values in the settings will actually be applied. As such, the values should be doubled for Shared Mode testing. Furthermore, note that in Shared Mode these values are being ADDED to already naturally occuring latency from being online.
Third party software
When using the release version of the fusion.dll, it is still possible to simulate adverse network conditions by using a third party app to delay and disrupt network traffic.
For Windows, Clumsy is the most commonly used and recommended third-party app for simulating adverse network conditions.
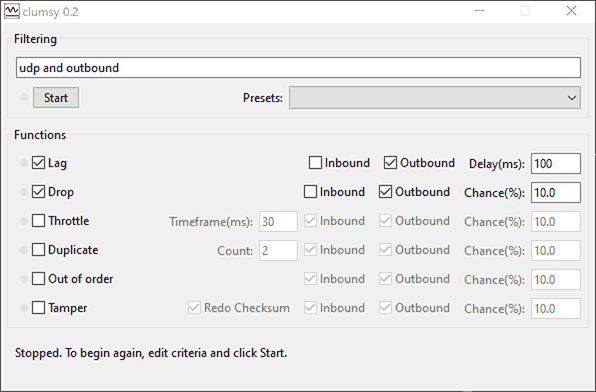
A filtering string of 'udp and outbound' should work for most use cases. For more information and details on the specifics please refer to the Clumsy documentation. N.B.: The port and network IP address in use have to be known.
Back to top