Impostor

Overview
HostMode topology.The Fusion Impostor demonstrates an approach on how to develop the coreloop of a social deduction game for up to 10 players, as well as how to integrate and handle communication with the Photon Voice SDK with a Fusion project. Fore more information on Photon Voice please see the Voice page in the manual.
This sample implements a networked state machine to facilitate the synchronization and handling of game states
Some of the highlights of this sample are:
- Voice communication in the pre-grame lobby and in-game
- Fully networked game state machine and system encompassing pre-game, play, meetings, and post-game outcomes
- Shared interaction points such as task stations and crewmate bodies
- Customizable game settings (number of impostors, movement speed, player collision, etc)
- Synchronized state of objects in the world like doors
- A variety of crewmate tasks built upon a modular interaction system
- Using Photon Voice to provide handle a variety of voice communication types
- Setting up rooms as a host using codes for clients to join
- Region settings, nickname, and microphone selection


Technical Info
- Unity 2021.3
Before You Start
To run the sample
- Create a Fusion AppId in the PhotonEngine Dashboard and paste it into the
App Id Fusionfield in Real Time Settings (reachable from the Fusion menu). - Create a Voice AppId in the PhotonEngine Dashboard and paste it into the
App Id Voicefield in Real Time Settings - Then load the
Launchscene and pressPlay.
Download
| Version | Release Date | Download | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1.3 | Oct 21, 2022 | Fusion Impostor 1.1.3 Build 5 | ||
Folder Structure
The main Scripts folder /Scripts has a subfolder called Networkingwhich encompasses the main networking implementations in the sample, as well as the Networked State Machine. The other subfolders such as Player and Managers contain the logic for gameplay behaviours and management respectively.
PlayerRegistry
The PlayerRegistry stores a reference to each player in the room, and provides utility methods for selecting and performing actions on one or many players.
GameState
The flow and behaviour of the game logic is controlled by the GameState NetworkBehaviour. The GameState defines an enum for the phases of the game, which the networked StateMachine uses as its states.
StateMachine<T> defines a StateHooks class with 3 fields: onEnter, onExit, and onUpdate. When using the StateMachine class, each enum state may have StateHooks defining what happens upon entering, exiting, and while actively staying in the state.
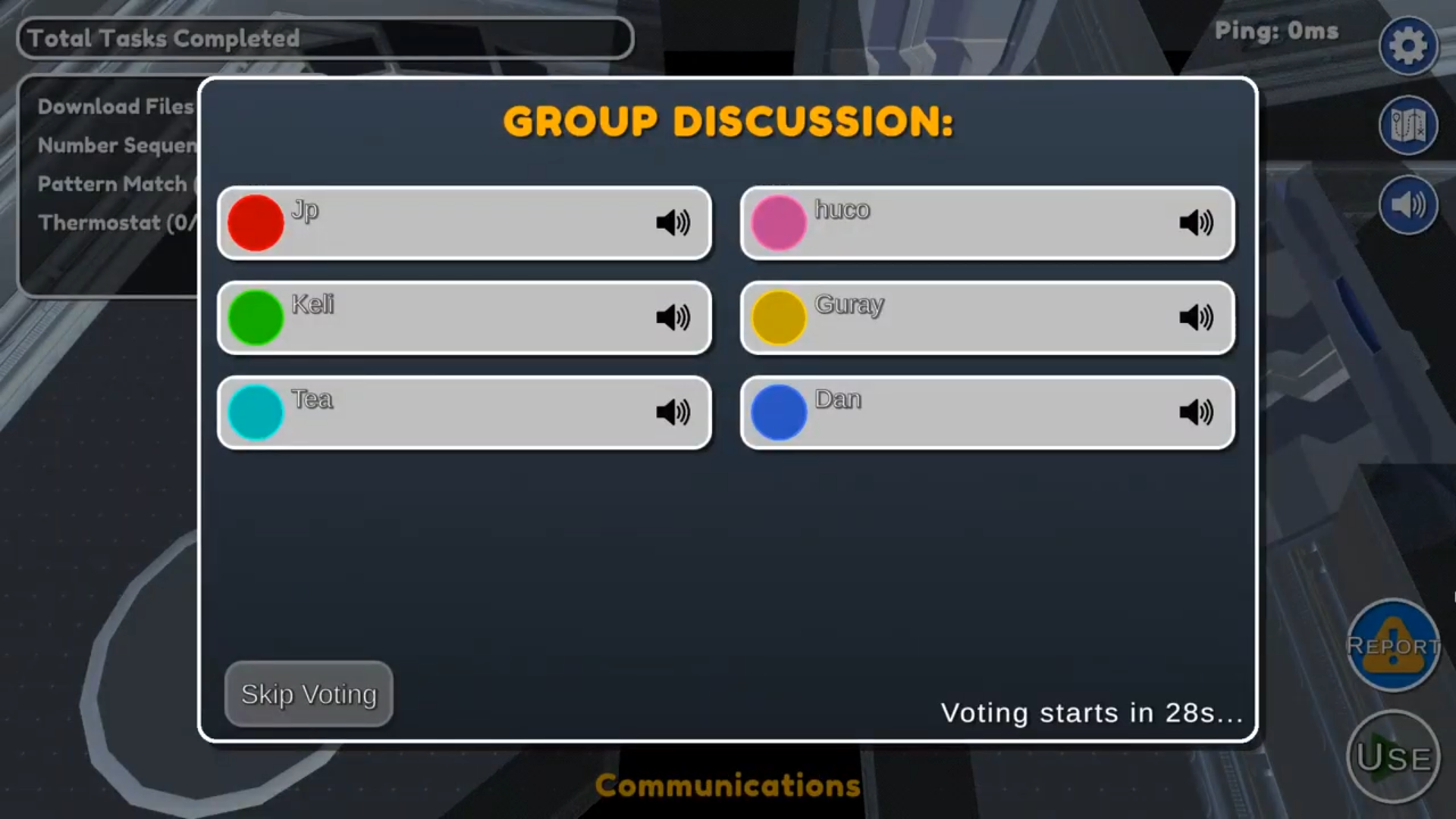
Getting Into a Game
Users can either join or host a room using a room code. Entering a room code is optional if the user chooses to host. Once in a room, the code to join will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
runner.SessionInfo.Name.The NetworkStartBridge serves as an intermediary to NetworkDebugStart. StartHost() will get a random 4 character string from RoomCode if a specific code is not specified.
Pre-Game
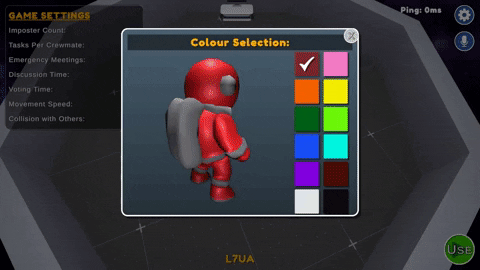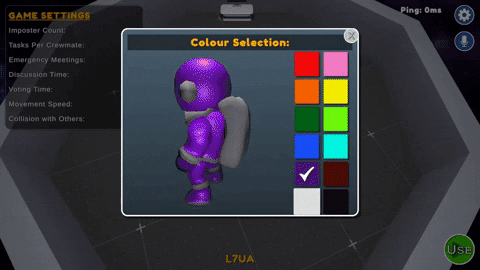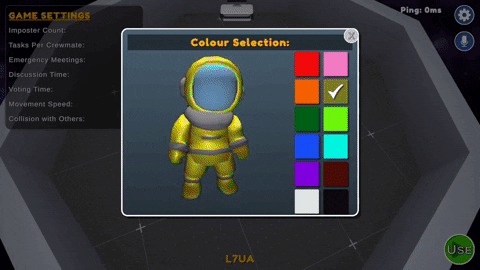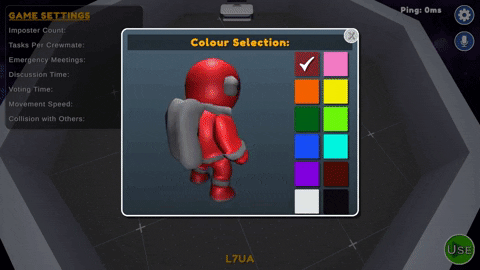
During the pre-game phase, players can choose to set their color from the table in the center of the lobby area, select their preferred microphone device from the settings. The host can customize the game settings and is responsible for starting the game.
Handling Input
Networked inputs are polled in the PlayerInputBehaviour.cs script. It is also here that input blocking is done. Additionally, server-side checks are done in PlayerMovement.cs before carrying out inputs.
Local input polling is done using the FixedInput.cs class.
Keyboard
- WASD to walk
- E to interact
- Keypad Enter to start game (as host, during pre-game only)
Mouse
- Left click to walk
- Click the buttons in the UI to interact
The Player
The Players's behaviour is defined by three different components:
PlayerObject: holds a reference to thePlayerRefthis object is associated with, and contains the player's index in the room, their nickname, and selected color. ThePlayerObjectis also the entry point to call theRpc_Killmethod.PlayerMovement: responsible for player locomotion and input. It also holds gameplay-essential data and methods - notably theIsDead,IsSuspect, andEmergencyMeetingUsesproperties.PlayerData: the visual component of the player. It primarily handles the materials, sets animator properties and instantiates the nickname UI.
Interactables
- Color Kiosk : Located on the center table in the Pre-Game room. Players can select from any of 12 preset colors which have not been taken by another player.
- Settings Kiosk : Located at the top of the Pre-Game room, the host can select the game settings and start the game from here
- Emergency Button : the emergency button can be pressed a limited amount of times per round to call a meeting
- Tasks : 14 task stations featuring 5 unique task minigames are placed throughout the map for crewmates to complete
- Bodies : the body of a murdered player can be reported to call a meeting for free by crewmates, or impostors who are trying to cover their tracks
Tasks
Task stations can be found throughout the map. Crewmates can interact with these when they are within range.
- Thermostat (
TemperatureTask.cs) : Make the two numbers equal by pushing the up and down arrows - Sliders (
SlidersTask.cs) : Drag each slider to align with the red outline. They will become locked when positioned correctly. - Pattern Match (
PatternMatchTask.cs) : Push buttons on the right panel matching the sequence of lights that flash on the left panel. - Number Sequence (
NumberSequenceTask.cs) : Push each number in ascending numerical order (1-10) - Download Files (
DownloadTask.cs) : Push the Download button and wait for the bar to fill in order to complete it.
Voice
For Voice 2 integration in Fusion Impostor the two scripts provided by Photon Voice 2 are used:
- FusionVoiceNetwork is added to
PrototypeRunnerprefab. - VoiceNetworkObject is used on the
Playerprefab, with aSpeakeras a child of the given prefab too.